Supply: OpenAI’s DALL·E 2 with immediate “a hyperrealistic image of a robotic studying the information on a laptop computer at a espresso store”
Welcome to the 4th version of Robo-Perception, a biweekly robotics information replace! On this put up, we’re excited to share a spread of recent developments within the area and spotlight robots’ progress in areas like cell functions, cleansing, underwater mining, flexibility, human well-being, despair remedies, and human interactions.
Simplified cell robotic conduct variations
On the earth of system adaptions, researchers from Eindhoven College of Expertise have launched a technique that bridges the hole between software builders and management engineers within the context of cell robots’ conduct adaptation. This strategy leverages symbolic descriptions of robots’ conduct, often known as “conduct semantics,” and interprets them into management actions by means of a “semantic map.” This innovation goals to simplify movement management programming for autonomous cell robotic functions and facilitate integration throughout numerous distributors’ management software program. By establishing a structured interplay layer between software, interplay, and management layers, this system might streamline the complexity of cell robotic functions, doubtlessly resulting in extra environment friendly underground exploration and navigation methods.
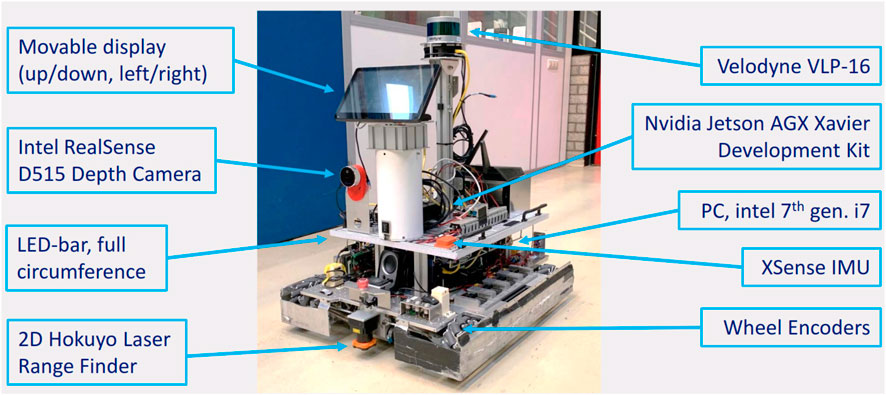
The frontal perspective of the cell platform (showcases {hardware} elements with blue arrows). Supply.
New robotic for family clean-ups
Talking of useful robots, Princeton College has created a robotic named TidyBot to deal with the problem of family tidying. In contrast to easy duties corresponding to shifting objects, real-world cleanup requires a robotic to distinguish between objects, place them accurately, and keep away from damaging them. TidyBot accomplishes this by means of a mix of bodily dexterity, visible recognition, and language understanding. Geared up with a cell robotic arm, a imaginative and prescient mannequin, and a language mannequin, TidyBot can determine objects, place them in designated places, and even infer correct actions with an 85% accuracy charge. The success of TidyBot demonstrates its potential to deal with advanced family duties.

TidyBot in work. Supply.
Deep sea mining robots
Shifting our focus to underwater environments, researchers are addressing the effectivity hurdles confronted in deep-sea mining by means of progressive path planning for autonomous robotic mining autos. With deep-sea manganese nodules holding important potential, these robotic autos are important for his or her assortment. By refining path planning strategies, the researchers purpose to enhance the effectivity of those autos in traversing difficult underwater terrains whereas avoiding obstacles. This improvement might result in simpler and accountable useful resource extraction from the ocean ground, contributing to the sustainable utilization of priceless mineral sources.
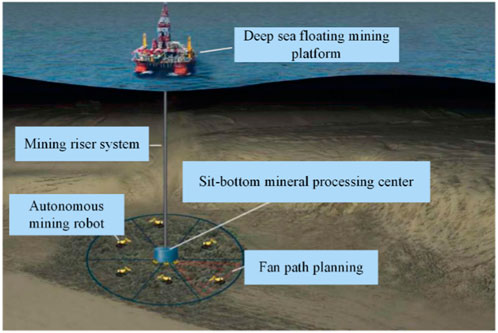
Diagram depicting the operational framework of the deep-sea mining system. Supply.
Superior gentle robots with dexterity and adaptability
Regarding the area of robotic movement, just lately researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong College have developed small-scale gentle robots with exceptional dexterity, enabling speedy and reversible adjustments in movement route and form reconfiguration. These robots, powered by an lively dielectric elastomer synthetic muscle and a novel chiral-lattice foot design, can change route throughout quick motion with a single voltage enter. The chiral-lattice foot generates numerous locomotion behaviors, together with ahead, backward, and round movement, by adjusting voltage frequencies. Moreover, combining this structural design with form reminiscence supplies permits the robots to carry out advanced duties like navigating slim tunnels or forming particular trajectories. This innovation opens the door to next-generation autonomous gentle robots able to versatile locomotion.
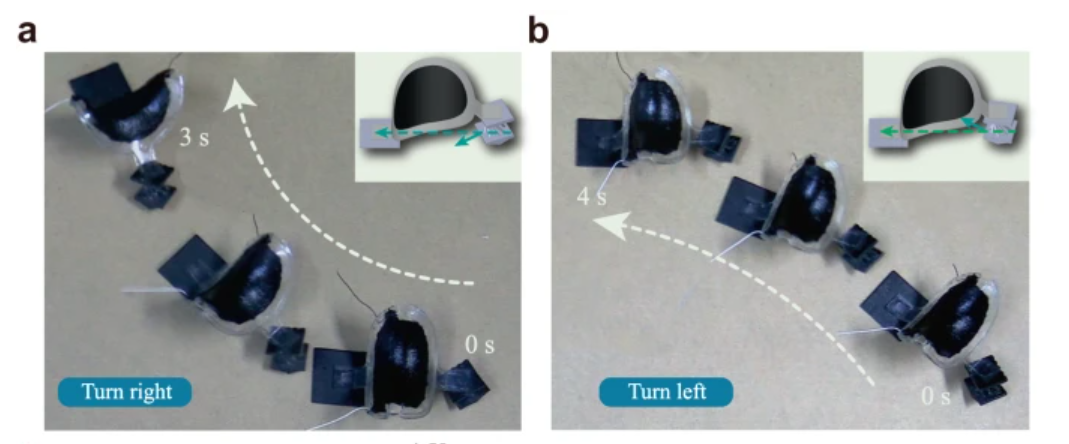
The gentle robotic achieves round movement in both proper or left instructions by positioning the lattice foot in the direction of the respective sides. Supply.
Robotic canine utilized to consolation sufferers
Turning our focus to robotic use within the healthcare area, Stanford college students, together with researchers and docs, have partnered with AI and robotics trade leaders to showcase new robotic canine designed to work together with pediatric sufferers at Lucile Packard Youngsters’s Hospital. Sufferers on the hospital had the chance to have interaction with the playful robots, demonstrating the potential advantages of those mechanical pets for kids’s well-being throughout their hospital stays. The robots, known as Pupper, have been developed by undergraduate engineering college students and operated utilizing handheld controllers. The aim of the demonstration was to check the interplay between the robots and pediatric sufferers, exploring methods to boost the medical expertise and scale back nervousness.
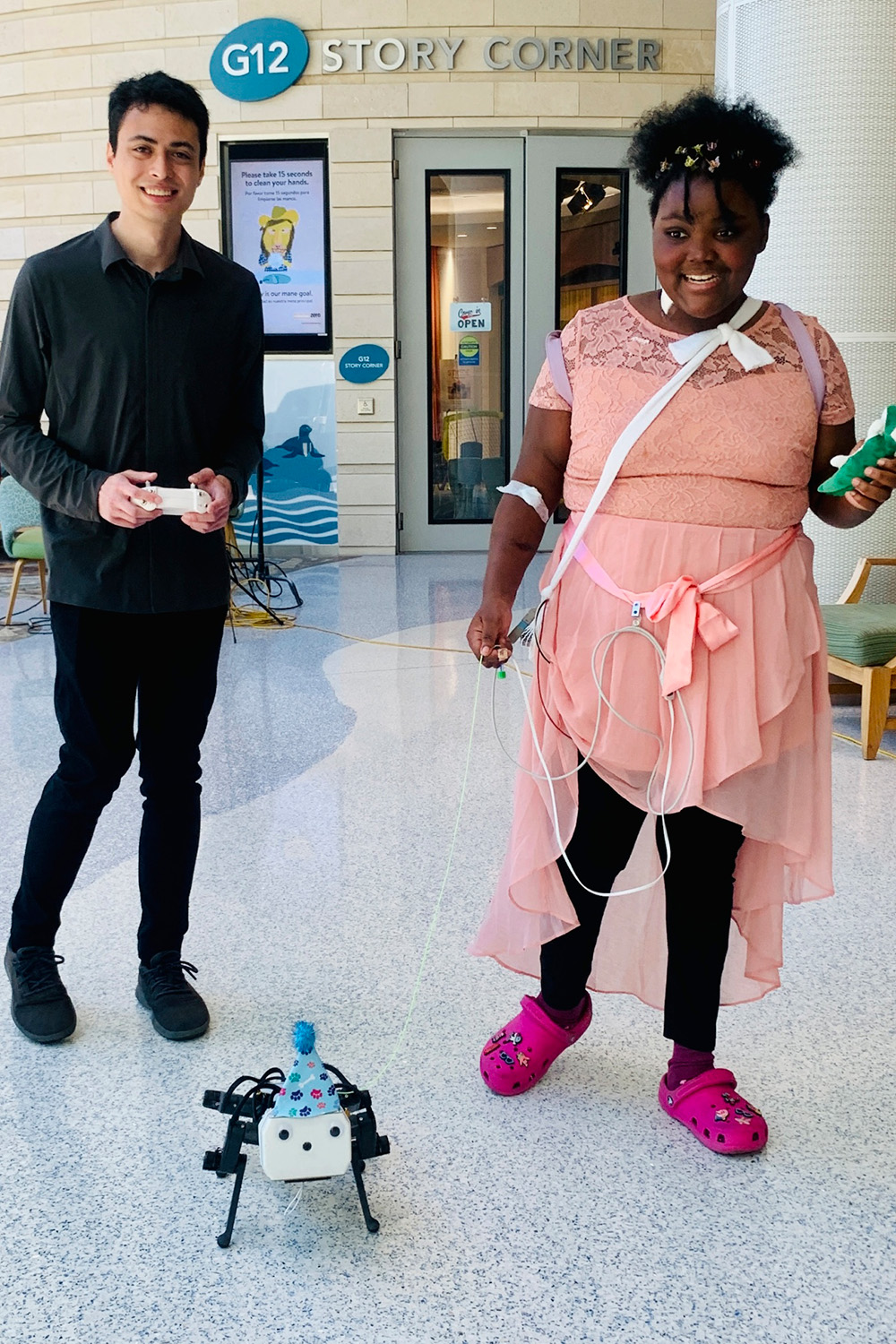

A affected person taking part in with the robotic canine. Supply.
Robotic improvements might assist with despair
Alongside the identical traces as bettering well-being, a current pilot research has explored the potential advantages of utilizing robotics in transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) for treating despair. Researchers led by Hyunsoo Shin developed a customized TMS robotic designed to enhance the accuracy of TMS coil placement on the mind, a important side of efficient remedy. By using the robotic system, they decreased preparation time by 53% and considerably minimized errors in coil positioning. The research discovered comparable therapeutic results on despair severity and regional cerebral blood stream (rCBF) between the robotic and guide TMS strategies, shedding gentle on the potential of robotic help in enhancing the precision and effectivity of TMS remedies.
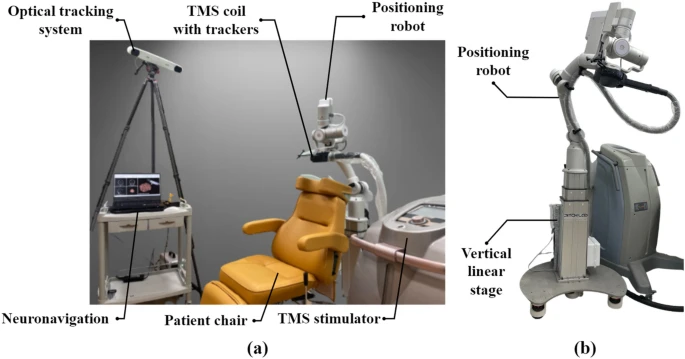
Configuration of the robotic repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) throughout the remedy facility, and robotic positioning system for automated coil placement. Supply.
Superior robotic eye analysis
Lastly, on this planet of human-robot enhancement, a research carried out by researchers from numerous establishments has explored the potential of utilizing robotic eyes as predictive cues in human-robot interplay (HRI). The research aimed to grasp whether or not and the way the design of predictive robotic eyes might improve interactions between people and robots. 4 several types of eye designs have been examined, together with arrows, human eyes, and two anthropomorphic robotic eye designs. The outcomes indicated that summary anthropomorphic robotic eyes, which mimic sure elements of human-like consideration, have been handiest at directing members’ consideration and triggering reflexive shifts. These findings recommend that incorporating summary anthropomorphic eyes into robotic design might enhance the predictability of robotic actions and improve HRI.
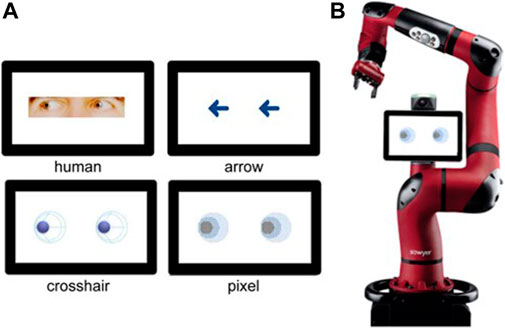
The 4 varieties of stimuli. The primary row showcases the human (left) and arrow (proper) stimuli. The second row shows the summary anthropomorphic robotic eyes. {Photograph} of the questionnaire’s topic, the cooperative robotic Sawyer. Supply.
The continual stream of progress seen throughout numerous domains underscores the adaptable and continuously progressing nature of robotics expertise, revealing novel pathways for its incorporation throughout a spectrum of industries. The gradual development within the realm of robotics displays persistent efforts and hints on the potential implications these strides may maintain for the long run.
Sources:
- Chen, H. L., Hendrikx, B., Torta, E., Bruyninckx, H., & van de Molengraft, R. (2023, July 10). Conduct adaptation for cell robots through semantic map compositions of constraint-based controllers. Frontiers.
- Princeton Engineering – Engineers clear up with TidyBot. (n.d.). Princeton Engineering. Retrieved August 30, 2023,
- Xie, Y., Liu, C., Chen, X., Liu, G., Leng, D., Pan, W., & Shao, S. (2023, July 12). Analysis on path planning of autonomous manganese nodule mining car primarily based on lifting mining system. Frontiers.
- Wang, D., Zhao, B., Li, X., Dong, L., Zhang, M., Zou, J., & Gu, G. (2023). Dexterous electrical-driven gentle robots with reconfigurable chiral-lattice foot design. Nature Communications, 14(1), 5067.
- College, S. (2023, August 1). Robo-dogs unleash pleasure at Stanford hospital. Stanford Report.
- Shin, H., Jeong, H., Ryu, W., Lee, G., Lee, J., Kim, D., Music, I.-U., Chung, Y.-A., & Lee, S. (2023). Robotic transcranial magnetic stimulation within the remedy of despair: a pilot research. Scientific Studies, 13(1), 14074.
- Onnasch, L., Schweidler, P., & Schmidt, H. (2023, July 3). The potential of robotic eyes as predictive cues in HRI-an eye-tracking research. Frontiers.
Shaunak Kapur
is a part of Robohub’s volunteering workforce, and soon-to-be senior in highschool (Texas). Shaun has been captivated by robotics from a younger age.

Shaunak Kapur
is a part of Robohub’s volunteering workforce, and soon-to-be senior in highschool (Texas). Shaun has been captivated by robotics from a younger age.
